Machine learning is a type of supervised or unsupervised artificial intelligence where software has the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. The adoption of machine learning is in full swing. For more than a decade, companies have used the power of machine learning to improve supply chain planning efficiencies and develop optimized supply chain decisions. Automatic model switching to improve forecast accuracy is just one of many examples of the early use of machine learning to continually tune the digital supply chain and optimally leverage physical supply chain network performance. Early results are driving the hype of machine learning applications to a fever pitch and there’s no question that machine learning is
a topic that supply chain practitioners should be actively investigating. The real question is, “Are we, as a profession, ready to embrace machine learning in an unsupervised fashion”? If so, what does that mean and
how do we get there?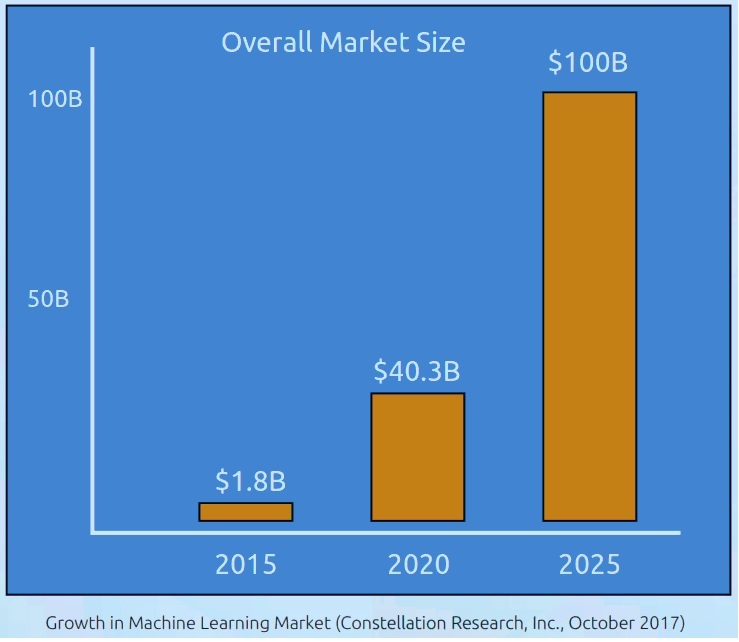 “CEOs expect supply chain leaders to prepare for DIGITAL BUSINESS and want to know how they intend to DEVELOP CAPABILITIES and use advanced technologies like artificial intelligence to create a flexible, agile and RESPONSIVE DIGITAL SUPPLY CHAIN.”
“CEOs expect supply chain leaders to prepare for DIGITAL BUSINESS and want to know how they intend to DEVELOP CAPABILITIES and use advanced technologies like artificial intelligence to create a flexible, agile and RESPONSIVE DIGITAL SUPPLY CHAIN.” THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MACHINE LEARNING AND BIG DATA
Terms like advanced analytics, algorithmic optimization, artificial intelligence and deep learning are often used interchangeably with machine learning. These terms are not the same, and it’s worthwhile to explain the differences:
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MACHINE LEARNING AND BIG DATA
Terms like advanced analytics, algorithmic optimization, artificial intelligence and deep learning are often used interchangeably with machine learning. These terms are not the same, and it’s worthwhile to explain the differences:
 BUILDING THE
MACHINE LEARNING PLATFORM
Does your supply chain platform support your plans to
harness machine learning capabilities? Here are a few
capabilities that your supply chain planning platform needs:
BUILDING THE
MACHINE LEARNING PLATFORM
Does your supply chain platform support your plans to
harness machine learning capabilities? Here are a few
capabilities that your supply chain planning platform needs: 1. Process Automation to free up resources to focus on higher value-added activities
2. Advanced Visualization for support of all analysis requirements
3. Support for All Levels of Analytic Maturity from descriptive through cognitive
4. In-Memory Processing for robust analysis and fast response times
5. Cloud-Based for fast deployment and flexible scalability
6. Configurable User Interface for cross-functional analysis requirements
7. Mobile Device Support for 24×7 access to supply chain operations
8. Master Data Management (MDM) for consistent, harmonized and managed data across your complete supply chain
1. Process Automation to free up resources to focus on higher value-added activities
2. Advanced Visualization for support of all analysis requirements
3. Support for All Levels of Analytic Maturity from descriptive through cognitive
4. In-Memory Processing for robust analysis and fast response times
5. Cloud-Based for fast deployment and flexible scalability
6. Configurable User Interface for cross-functional analysis requirements
7. Mobile Device Support for 24×7 access to supply chain operations
8. Master Data Management (MDM) for consistent, harmonized and managed data across your complete supply chain
 “CEOs expect supply chain leaders to prepare for DIGITAL BUSINESS and want to know how they intend to DEVELOP CAPABILITIES and use advanced technologies like artificial intelligence to create a flexible, agile and RESPONSIVE DIGITAL SUPPLY CHAIN.”
“CEOs expect supply chain leaders to prepare for DIGITAL BUSINESS and want to know how they intend to DEVELOP CAPABILITIES and use advanced technologies like artificial intelligence to create a flexible, agile and RESPONSIVE DIGITAL SUPPLY CHAIN.” THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MACHINE LEARNING AND BIG DATA
Terms like advanced analytics, algorithmic optimization, artificial intelligence and deep learning are often used interchangeably with machine learning. These terms are not the same, and it’s worthwhile to explain the differences:
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MACHINE LEARNING AND BIG DATA
Terms like advanced analytics, algorithmic optimization, artificial intelligence and deep learning are often used interchangeably with machine learning. These terms are not the same, and it’s worthwhile to explain the differences:
 BUILDING THE
MACHINE LEARNING PLATFORM
Does your supply chain platform support your plans to
harness machine learning capabilities? Here are a few
capabilities that your supply chain planning platform needs:
BUILDING THE
MACHINE LEARNING PLATFORM
Does your supply chain platform support your plans to
harness machine learning capabilities? Here are a few
capabilities that your supply chain planning platform needs: 1. Process Automation to free up resources to focus on higher value-added activities
2. Advanced Visualization for support of all analysis requirements
3. Support for All Levels of Analytic Maturity from descriptive through cognitive
4. In-Memory Processing for robust analysis and fast response times
5. Cloud-Based for fast deployment and flexible scalability
6. Configurable User Interface for cross-functional analysis requirements
7. Mobile Device Support for 24×7 access to supply chain operations
8. Master Data Management (MDM) for consistent, harmonized and managed data across your complete supply chain
1. Process Automation to free up resources to focus on higher value-added activities
2. Advanced Visualization for support of all analysis requirements
3. Support for All Levels of Analytic Maturity from descriptive through cognitive
4. In-Memory Processing for robust analysis and fast response times
5. Cloud-Based for fast deployment and flexible scalability
6. Configurable User Interface for cross-functional analysis requirements
7. Mobile Device Support for 24×7 access to supply chain operations
8. Master Data Management (MDM) for consistent, harmonized and managed data across your complete supply chain









